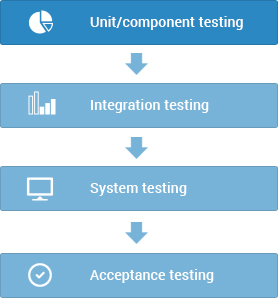
Unit/component testing
Unit Testing is a level of the software testing process where individual units/components of a software/system are tested. The purpose is to validate that each unit of the software performs as designed.
A unit is the smallest testable part of software. It usually has one or a few inputs and usually a single output. In procedural programming a unit may be an individual program, function, procedure, etc. In object-oriented programming, the smallest unit is a method, which may belong to a base/super class, abstract class or derived/child class. (Some treat a module of an application as a unit. This is to be discouraged as there will probably be many individual units within that module.)
Unit testing frameworks, drivers, stubs and mock or fake objects are used to assist in unit testing.
- METHOD
- Unit Testing is performed by using the White Box Testing method.
- When is it performed?
- Unit Testing is the first level of testing and is performed prior to Integration Testing.
- Who performs it?
- Unit Testing is normally performed by software developers themselves or their peers. In rare cases it may also be performed by independent software testers.
- TASKS
-
- Unit Test Plan
- Prepare
- Review
- Rework
- Baseline
- Unit Test Cases/Scripts
- Prepare
- Review
- Rework
- Baseline
- Unit Test
- Perform
- Definition by ISTQB
- unit testing: See component testing.
component testing: The testing of individual software components.